Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark3.x 新特性 AQE的理解和介绍
张晓龙 / 2023-04-19
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark3.x 主节点 Master 和 Worker 节点 启动过程分析
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark RPC 架构设计和Akka架构以及基于Spark RPC框架的通信代码演示
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark 2.4 to 3.4 releases notes on spark core and SQL
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark RPC 框架的发展历史和RPC核心类图关系
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark 基础&重要的概念(base and important conception)
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark3.x 新特性 AQE的理解和介绍
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Kyuubi1.7 Overview和部署核心参数调优
The discovery of Spark 系列文章目前共:7 篇
 Spark3.x 新特性 AQE(Adaptive Query Execution (AQE) in Spark 3)的理解和介绍
Spark3.x 新特性 AQE(Adaptive Query Execution (AQE) in Spark 3)的理解和介绍
多Join场景下的Cost-based Join Reorder问题,Spark 应用 CBO 策略解决问题,但是CBO优化策略需要预先处理信息(行数、去重后的行数、空值、最大最小值等),如果预处理信息失效过期,spark 应用过期数据有概率降低任务运行效率,在 spark3.0 新版本中,加入了 AQE 特性,AQE在执行过程中统计数据,并动态地调节执行计划,从而解决了该问题(Adaptive query execution (AQE) is query re-optimization that occurs during query execution)。
The Adaptive Query Execution (AQE) framework
什么时候去重新计算优化执行计划?
– > 每个Query Stage会产出中间结果,当且仅当该stage及其并行的所有stage都执行完成后,下游的Query Stage才能被执行。
– > 当上游部分stage执行完成,partitions的统计数据也获取到了,并且下游还未开始执行,这就给AQE提供了reoptimization的机会。(物化点(Materialization Points),并且用"Query Stages"来代表那些被物化点所分割的小片段。)
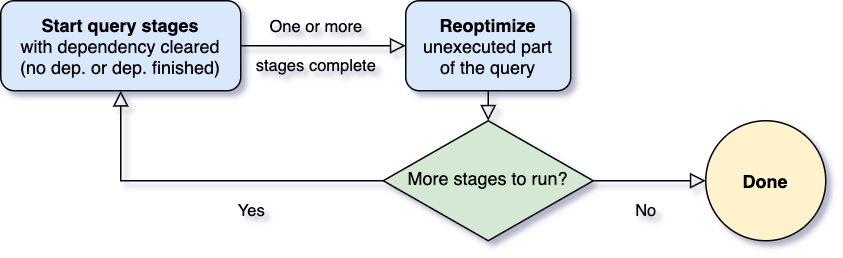
执行过程:
在查询开始时,生成完了执行计划 1、AQE框架会找到并执行那些不存在上游的stages。一旦这些stage有一个或多个完成,AQE框架就会将其在physical plan中标记为完成,并根据已完成的stages提供的执行数据来更新整个logical plan。 2、基于这些新产出的统计数据,AQE框架会执行optimizer,根据一系列的优化规则来进行优化; 3、AQE框架还会执行生成普通physical plan的optimizer以及自适应执行专属的优化规则,例如分区合并、数据倾斜处理等。 4、我们就获得了最新优化过的执行计划和一些已经执行完成的stages,至此为一次循环。 5、接着只需要继续重复上面的步骤,直到整个query都跑完
Spark 3.x AQE框架拥三个特性
- Dynamically coalescing shuffle partitions
- Dynamically switching join strategies
- Dynamically optimizing skew joins
1、动态合并shuffle partition(Dynamically coalescing shuffle partitions)
One key property of shuffle is the number of partitions。shuffle partitions过程中,partition 过多和过少都会有拖慢查询
- partition 过多:每个partition数据量就会很少,就会产生很多额外的网络开销(inefficient I/O pattern),并且影响Spark task scheduler,从而拖慢查询
- partition 过少:每个partition数据量就会过多,可能就会导致大量数据要落到磁盘上,从而拖慢了查询
解法:为了解决该问题,我们在最开始设置相对较大的shuffle partition个数,通过执行过程中shuffle文件的数据来合并相邻的小partitions。
case from 【databriks】:例如一下 SQL,
SELECT max(i)FROM tbl GROUP BY j;
假设该表只有2 个 partition ,且数据量不大。如果我们初始设置shuffle partition = 5, 分别看下没有启动 AQE 和启动 AQE 的区别
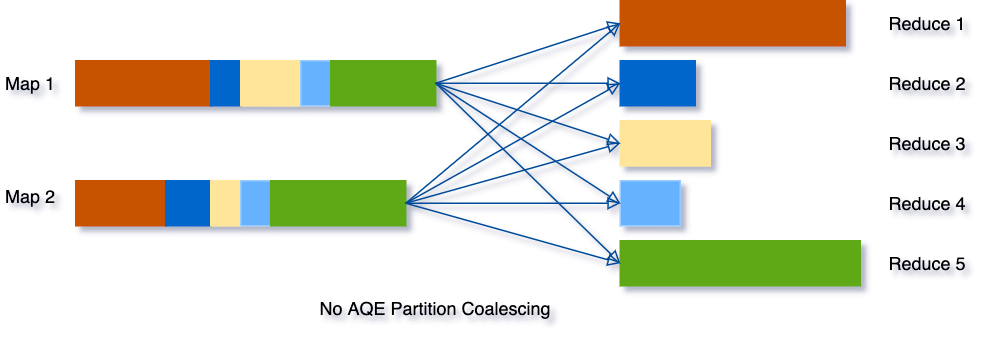
开启 AQE 后,将小的 partition 进行了合并

2、动态选择join策略 (Dynamically switching join strategies)
在Spark所支持的众多join中,broadcast hash join性能是最好的(one side of the join can fit well in memory)。
因此,如果需要广播的表的预估大小小于了广播限制阈值,那么我们就应该将其设为broadcast hash join。但是,对于表的大小估计不当会导致决策错误,比如join表有很多的filter(容易把表估大)或者join表有很多其他算子(容易把表估小),而不仅仅是全量扫描一张表。
由于AQE拥有精确的上游统计数据,因此可以解决该问题。比如下面这个例子,右表的实际大小为15M,而在该场景下,经过filter过滤后,实际参与join的数据大小为8M,小于了默认broadcast阈值10M,应该被广播。
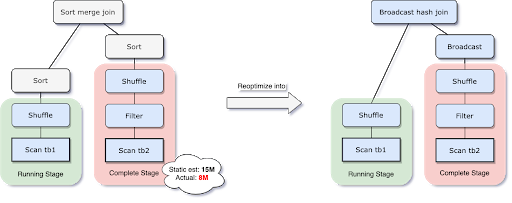
在我们执行过程中转化为broadcast hash join的同时,我们甚至可以将传统shuffle优化为本地shuffle(例如shuffle读在mapper而不是基于reducer)来减小网络开销。
3、动态优化存在数据倾斜的join (Dynamically optimizing skew joins)
数据倾斜是由于集群上数据在分区之间分布不均匀所导致的,它会拉慢join场景下整个查询。
AQE根据shuffle文件统计数据自动检测倾斜数据,将那些倾斜的分区打散成小的子分区,然后各自进行join (AQE skew join optimization detects such skew automatically from shuffle file statistics)。
可以看下这个场景,Table A join Table B,其中Table A的partition A0数据远大于其他分区。
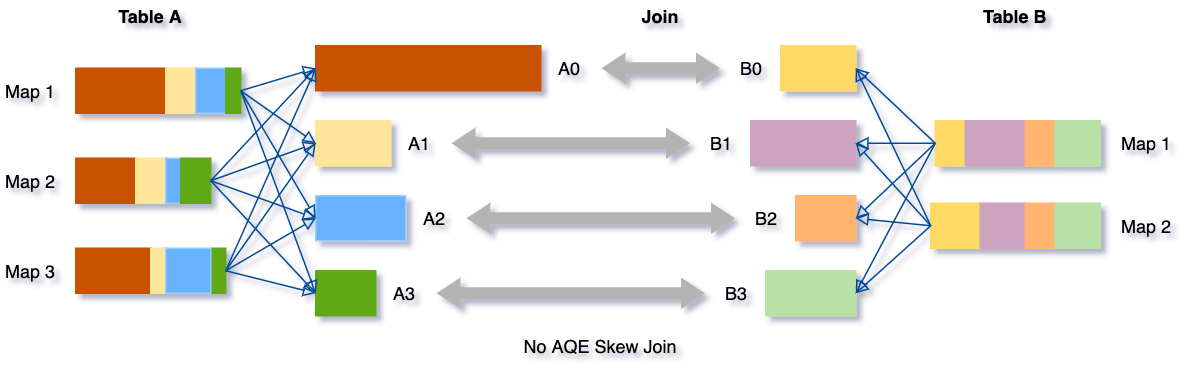
AQE会将partition A0切分成2个子分区,并且让他们独自和Table B的partition B0进行join。
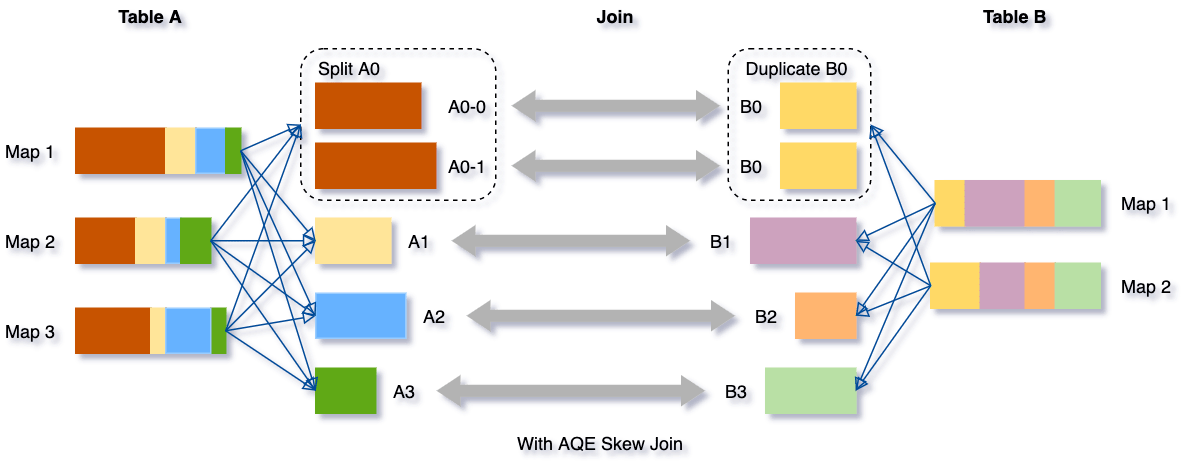
如果不做这个优化,SMJ将会产生4个tasks并且其中一个执行时间远大于其他。经优化,这个join将会有5个tasks,但每个task执行耗时差不多相同,因此个整个查询带来了更好的性能。
AQE通过减少了对静态统计数据的依赖,成功解决了Spark CBO的一个难以处理的trade off(生成统计数据的开销和查询耗时)以及数据精度问题。相比之前具有局限性的CBO,现在就显得非常灵活。
AQE 特性验证Case
基础环境准备
我在 kyuubi1.7 beeline 连接下进行测试,下面进行数据坏境构造。
1、环境变量设置(我的 kyuubi 已经默认开启 aqe 设置,这里主要是minPartitionNum 的设置)
set spark.sql.adaptive.enabled = true;
-- For demo purpose only.
-- Not necesary in real-life usage.
set spark.sql.adaptive.coalescePartitions.minPartitionNum = 1;
2、构造数据
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS aqe_demo_db;
USE aqe_demo_db;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS items;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS sales;
-- Create "items" table.
CREATE TABLE items
USING parquet
AS
SELECT id AS i_item_id,
CAST(rand() * 1000 AS INT) AS i_price
FROM RANGE(30000000);
-- Create "sales" table with skew.
-- Item with id 100 is in 80% of all sales.
CREATE TABLE sales
USING parquet
AS
SELECT CASE WHEN rand() < 0.8 THEN 100 ELSE CAST(rand() * 30000000 AS INT) END AS s_item_id,
CAST(rand() * 100 AS INT) AS s_quantity,
DATE_ADD(current_date(), - CAST(rand() * 360 AS INT)) AS s_date
FROM RANGE(1000000000);
表中数据样例:
Table items:
| i_item_id | i_price |
|---|---|
| 20000000 | 681 |
| 20000001 | 308 |
| 20000002 | 676 |
| 20000003 | 915 |
| 20000004 | 364 |
| 20000005 | 496 |
| 20000006 | 740 |
| 20000007 | 744 |
| 20000008 | 105 |
| 20000009 | 387 |
Table sales:
| s_item_id | s_quantity | s_date |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 44 | 2022-05-06 |
| 100 | 83 | 2022-06-11 |
| 23074207 | 92 | 2023-04-19 |
| 100 | 30 | 2022-05-30 |
| 100 | 30 | 2022-05-01 |
| 12853416 | 36 | 2022-08-30 |
| 100 | 70 | 2023-01-16 |
| 16579060 | 85 | 2023-04-19 |
| 100 | 59 | 2022-05-19 |
| 100 | 35 | 2022-11-01 |
验证特性
1、验证特性之一:Dynamically Coalesce Shuffle Partitions
-- Get the sums of sales quantity grouped by sales date.
-- The grouped result is very small.
SELECT s_date, sum(s_quantity) AS q
FROM sales
GROUP BY s_date
ORDER BY q DESC;
执行 sql 的结果:
Sample:
| s_date | q |
|---|---|
| 2022-11-26 | 137797897 |
| 2022-11-24 | 137775296 |
| 2022-11-10 | 137757195 |
| 2023-03-23 | 137747810 |
| 2022-05-18 | 137741420 |
| 2022-07-06 | 137738653 |
| 2023-03-04 | 137708403 |
| 2022-07-03 | 137704652 |
| 2022-04-25 | 137702356 |
| 2022-05-17 | 137700403 |
| 2023-04-18 | 137698493 |
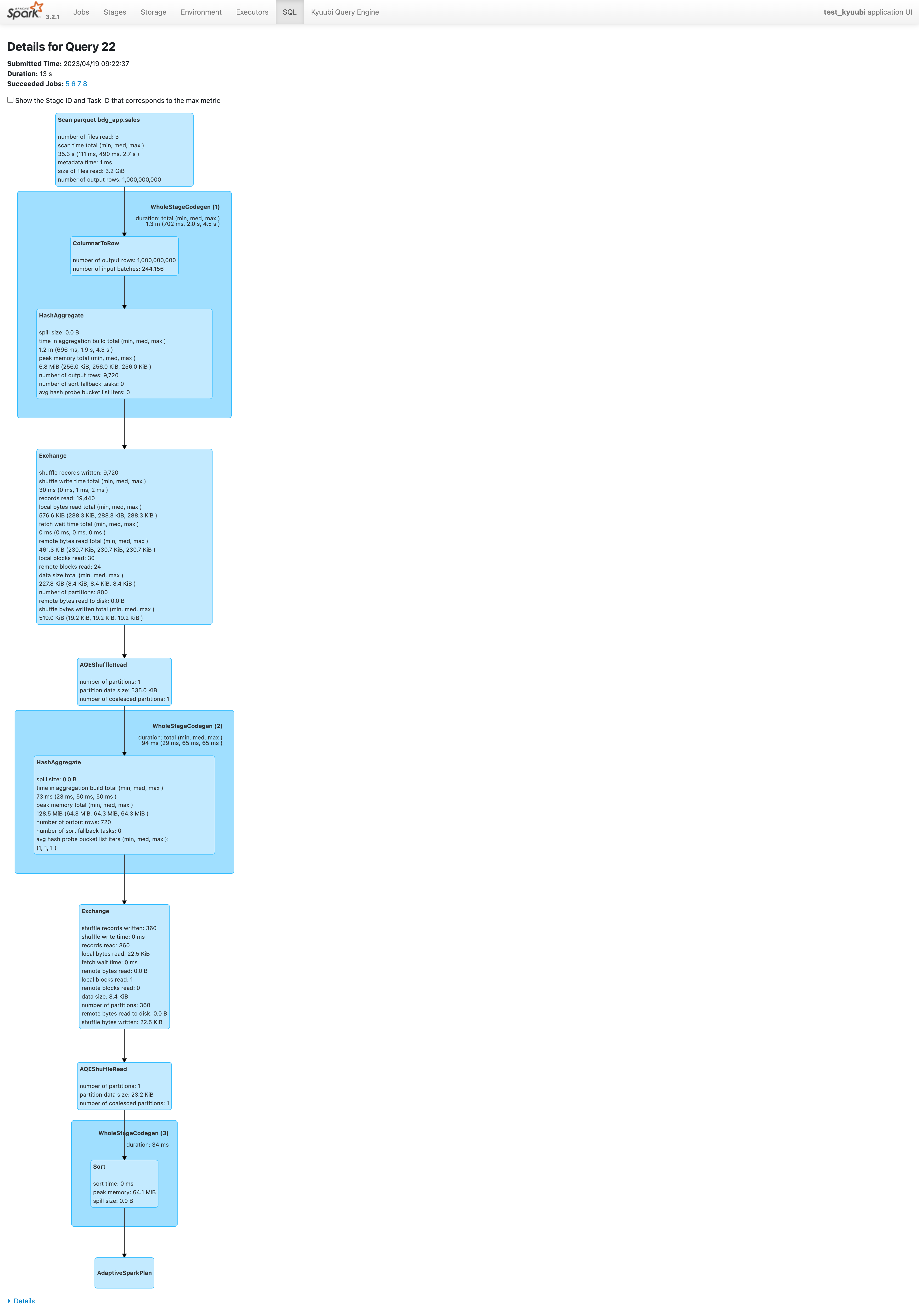
我们在 sparkUI 上看下 job执行情况
- The partition sizes after aggregation are very small: 22KB on average, 519KB in total (see the highlighted box shuffle bytes written).
- AQE combines these small partitions into one new partition (see the highlighted box AQEShuffleRead).
- 第一个exchange 阶段number of partitions: 800, AQEShuffleRead阶段:number of partitions: 1
- 第二个 exchage 阶段number of partitions: 360, AQEShuffleRead阶段:number of partitions: 1
2、验证特性之二:Dynamically Switch Join Strategies
-- Get total sales amount grouped by sales date for items with a price lower than 10.
-- The selectivity of the filter by price is not known in static planning, so the initial plan opts for sort merge join.
-- But in fact, the "items" table after filtering is very small, so the query can do a broadcast hash join instead.
-- Static explain shows the initial plan with sort merge join.
EXPLAIN FORMATTED
SELECT s_date, sum(s_quantity * i_price) AS total_sales
FROM sales
JOIN items ON s_item_id = i_item_id
WHERE i_price < 10
GROUP BY s_date
ORDER BY total_sales DESC;
执行explain sql 的结果:
+----------------------------------------------------+
| plan |
+----------------------------------------------------+
| == Physical Plan ==
AdaptiveSparkPlan (16)
+- Sort (15)
+- Exchange (14)
+- HashAggregate (13)
+- Exchange (12)
+- HashAggregate (11)
+- Project (10)
+- SortMergeJoin Inner (9)
:- Sort (4)
: +- Exchange (3)
: +- Filter (2)
: +- Scan parquet app.sales (1)
+- Sort (8)
+- Exchange (7)
+- Filter (6)
+- Scan parquet app.items (5)
(1) Scan parquet app.sales
Output [3]: [s_item_id#87, s_quantity#88, s_date#89]
Batched: true
Location: InMemoryFileIndex [xxxx/hive/warehouse/app.db/sales]
PushedFilters: [IsNotNull(s_item_id)]
ReadSchema: struct<s_item_id:int,s_quantity:int,s_date:date>
(2) Filter
Input [3]: [s_item_id#87, s_quantity#88, s_date#89]
Condition : isnotnull(s_item_id#87)
(3) Exchange
Input [3]: [s_item_id#87, s_quantity#88, s_date#89]
Arguments: hashpartitioning(cast(s_item_id#87 as bigint), 800), ENSURE_REQUIREMENTS, [id=#238]
(4) Sort
Input [3]: [s_item_id#87, s_quantity#88, s_date#89]
Arguments: [cast(s_item_id#87 as bigint) ASC NULLS FIRST], false, 0
(5) Scan parquet app.items
Output [2]: [i_item_id#80L, i_price#81]
Batched: true
Location: InMemoryFileIndex [xxxx/user/hive/warehouse/app.db/items]
PushedFilters: [IsNotNull(i_price), LessThan(i_price,10), IsNotNull(i_item_id)]
ReadSchema: struct<i_item_id:bigint,i_price:int>
(6) Filter
Input [2]: [i_item_id#80L, i_price#81]
Condition : ((isnotnull(i_price#81) AND (i_price#81 < 10)) AND isnotnull(i_item_id#80L))
(7) Exchange
Input [2]: [i_item_id#80L, i_price#81]
Arguments: hashpartitioning(i_item_id#80L, 800), ENSURE_REQUIREMENTS, [id=#239]
(8) Sort
Input [2]: [i_item_id#80L, i_price#81]
Arguments: [i_item_id#80L ASC NULLS FIRST], false, 0
(9) SortMergeJoin
Left keys [1]: [cast(s_item_id#87 as bigint)]
Right keys [1]: [i_item_id#80L]
Join condition: None
(10) Project
Output [3]: [s_quantity#88, s_date#89, i_price#81]
Input [5]: [s_item_id#87, s_quantity#88, s_date#89, i_item_id#80L, i_price#81]
(11) HashAggregate
Input [3]: [s_quantity#88, s_date#89, i_price#81]
Keys [1]: [s_date#89]
Functions [1]: [partial_sum((s_quantity#88 * i_price#81))]
Aggregate Attributes [1]: [sum#117L]
Results [2]: [s_date#89, sum#118L]
(12) Exchange
Input [2]: [s_date#89, sum#118L]
Arguments: hashpartitioning(s_date#89, 800), ENSURE_REQUIREMENTS, [id=#246]
(13) HashAggregate
Input [2]: [s_date#89, sum#118L]
Keys [1]: [s_date#89]
Functions [1]: [sum((s_quantity#88 * i_price#81))]
Aggregate Attributes [1]: [sum((s_quantity#88 * i_price#81))#116L]
Results [2]: [s_date#89, sum((s_quantity#88 * i_price#81))#116L AS total_sales#110L]
(14) Exchange
Input [2]: [s_date#89, total_sales#110L]
Arguments: rangepartitioning(total_sales#110L DESC NULLS LAST, 800), ENSURE_REQUIREMENTS, [id=#249]
(15) Sort
Input [2]: [s_date#89, total_sales#110L]
Arguments: [total_sales#110L DESC NULLS LAST], true, 0
(16) AdaptiveSparkPlan
Output [2]: [s_date#89, total_sales#110L]
Arguments: isFinalPlan=false
实际在执行 sql 时:
-- The runtime join stategy is changed to broadcast hash join.
SELECT s_date, sum(s_quantity * i_price) AS total_sales
FROM sales
JOIN items ON s_item_id = i_item_id
WHERE i_price < 10
GROUP BY s_date
ORDER BY total_sales DESC;
SQL 结果
| s_date | total_sales |
|---|---|
| 2022-11-30 | 1308323 |
| 2022-07-12 | 1305214 |
| 2022-09-05 | 1305038 |
| 2023-03-18 | 1294962 |
| 2022-11-15 | 1290920 |
| 2022-08-19 | 1289719 |
| 2023-01-26 | 1288687 |
| 2022-09-16 | 1288577 |
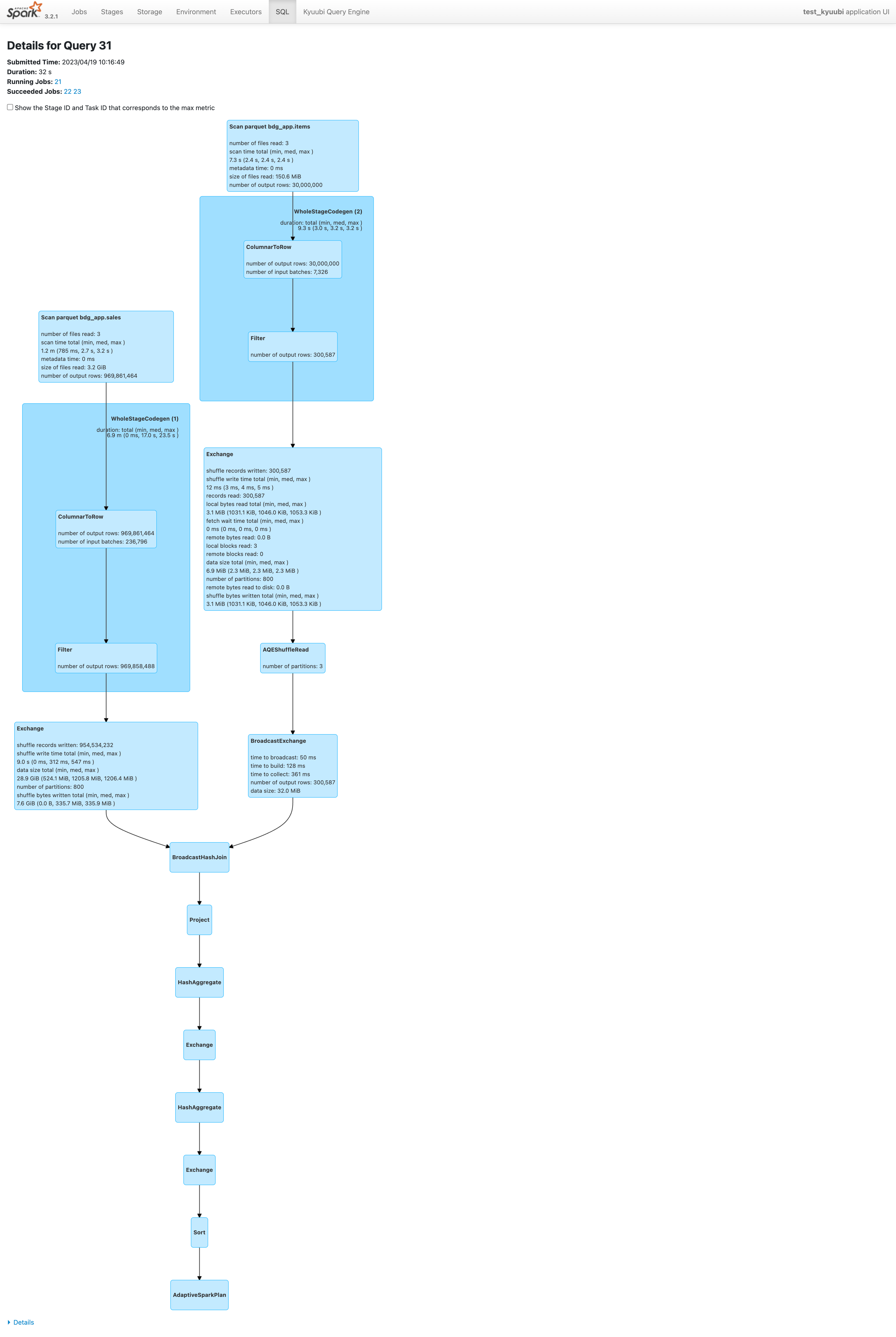
- The data size of the “items” table after filtering is very small 6.9 MiB (see the highlighted box data size).
- AQE changes the sort merge join to broadcast hash join at runtime (see the highlighted box BroadcastHashJoin).
我们看下job 实际执行情况
3、验证特性之三:Dynamically Optimize Skew Join
-- Get the total sales amount grouped by sales date.
-- The partition in the "sales" table containing value "100" as "s_item_id" is much larger than other partitions.
-- AQE splits the skewed partition into smaller partitions before joining the "sales" table with the "items" table.
SELECT s_date, sum(s_quantity * i_price) AS total_sales
FROM sales
JOIN items ON i_item_id = s_item_id
GROUP BY s_date
ORDER BY total_sales DESC;
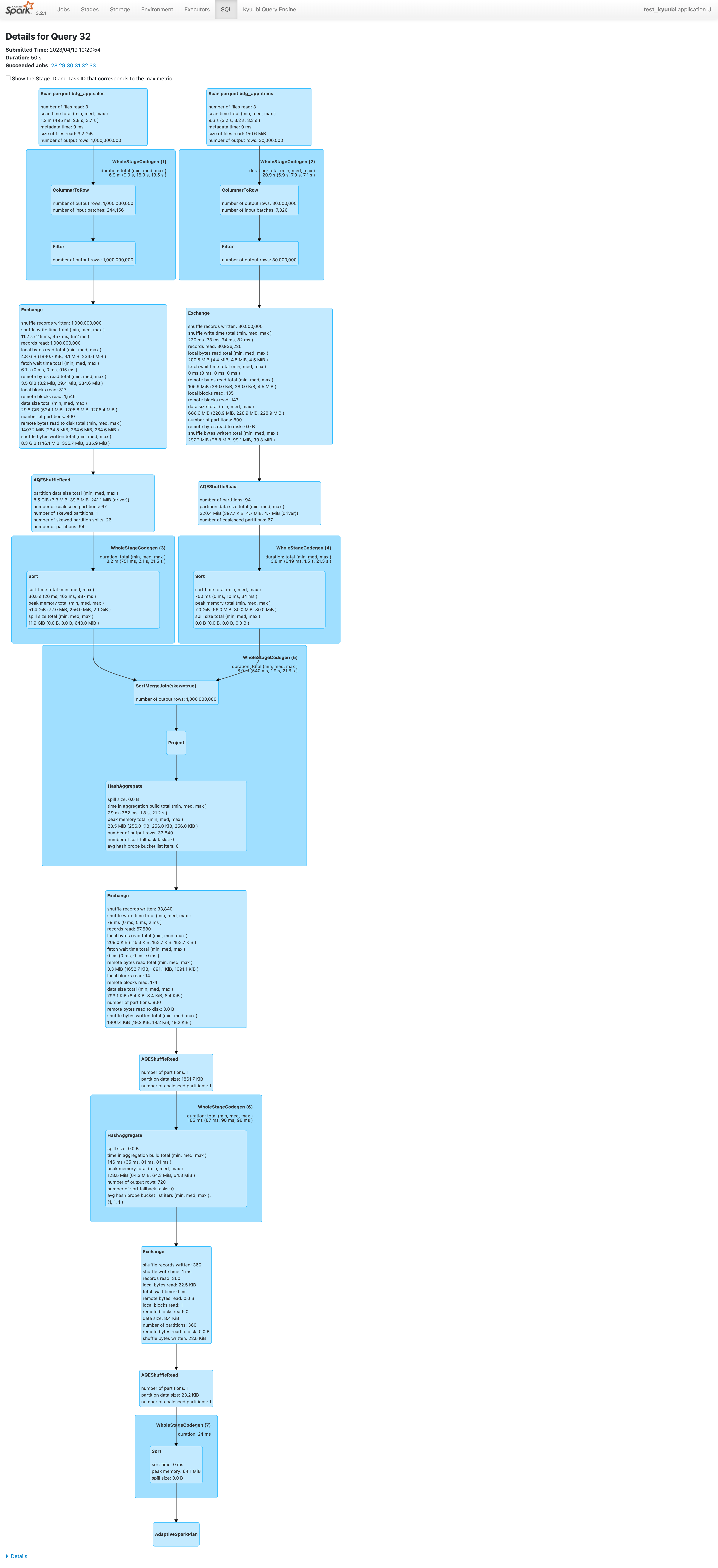
- There is a skewed partition from the “sales” table (see the highlighted box number of skewed partitions).
- AQE splits the skewed partition into smaller partitions (see the highlighted box number of skewed partition splits).
- The sort merge join operator is marked with a skew join flag (see the highlighted box SortMergeJoin(isSkew=true)).
在AQEShuffleRead阶段,
partition data size total (min, med, max )
8.5 GiB (3.3 MiB, 39.5 MiB, 241.1 MiB (driver))
number of coalesced partitions: 67
number of skewed partitions: 1
number of skewed partition splits: 26
number of partitions: 94
一些注意的坑
1、BoardcastJoin(阈值为 10M)会计算一些列的大小,由于 ORC 或者 parquet 格式有压缩存在,在实际执行过程数据会放到 7-10 倍,导致 driver OOM! 所有全局开启 AQE 的这个Dynamically Switch Join Strategies特性,需要注意这个!
相关资料
- Adaptive Query Execution: Speeding Up Spark SQL at Runtime
- databricks-Adaptive query execution
- Spark 3.0 - AQE浅析 (Adaptive Query Execution)
- Spark AQE SkewedJoin 在字节跳动的实践和优化
- Adaptive Query Execution (AQE) in Spark 3 with Example : What Every Spark Programmer Must Know
- [Spark 3.0 - AQE浅析 (Adaptive Query Execution)
–2023.4.19 更新内容
(2022.8)In Databricks Runtime 7.3 LTS and above, AQE is enabled by default. It has 4 major features:
- Dynamically changes sort merge join into broadcast hash join
- Dynamically coalesces partitions (combine small partitions into reasonably sized partitions) after shuffle exchange. Very small tasks have worse I/O throughput and tend to suffer more from scheduling overhead and task setup overhead. Combining small tasks saves resources and improves cluster throughput.
- Dynamically handles skew in sort merge join and shuffle hash join by splitting (and replicating if needed) skewed tasks into roughly evenly sized tasks.
- Dynamically detects and propagates empty relations.
前三个特性对应文章上部分的三个特性。最后一个拿出来看看是什么?
Dynamically detect and propagate empty relations: part of (or entire) the plan is replaced by node LocalTableScan with the relation field as empty.
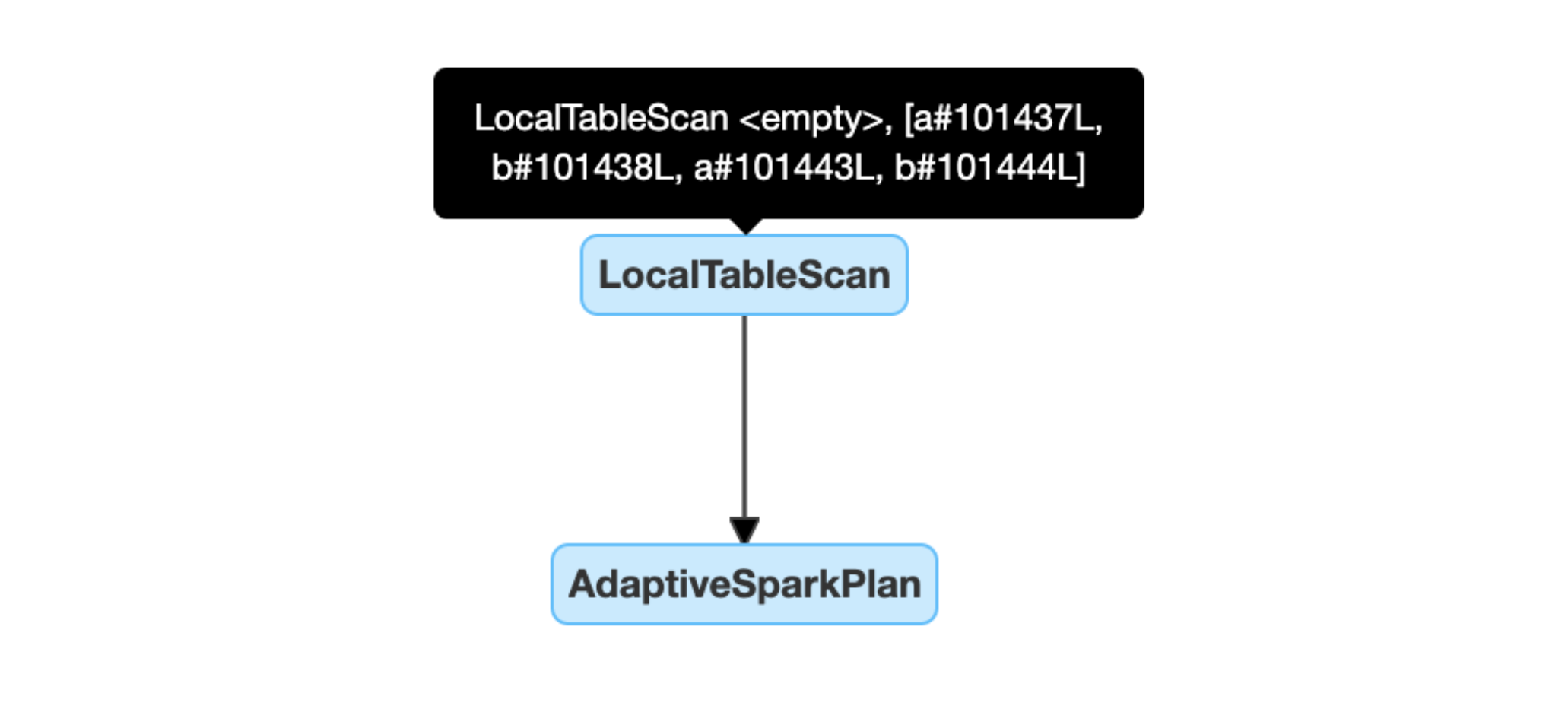
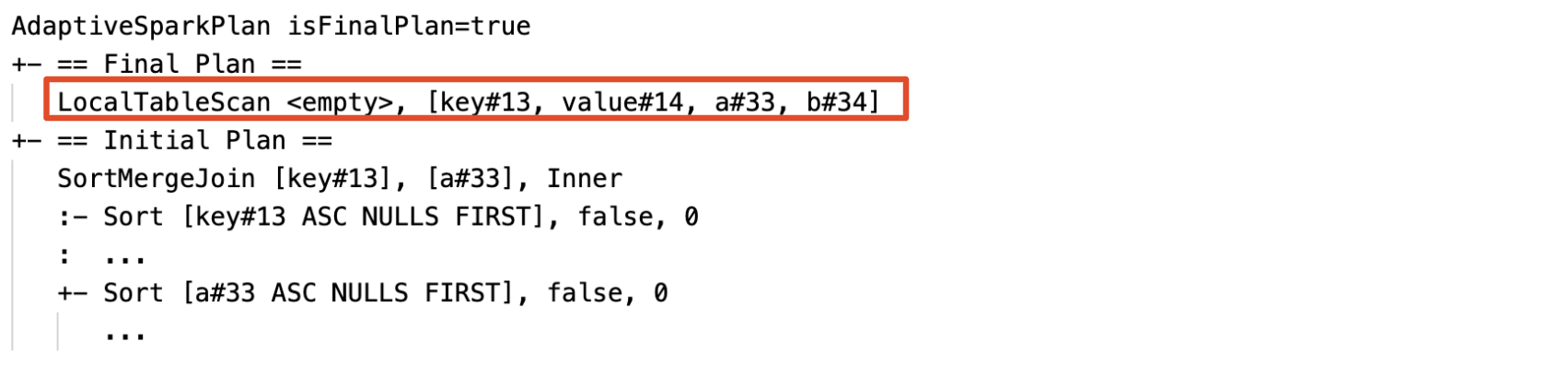
这个优化存在于 spark 的逻辑计划优化中,在 spark3.2.1版本code:
Batch("LocalRelation", fixedPoint,
ConvertToLocalRelation,
PropagateEmptyRelation,
// PropagateEmptyRelation can change the nullability of an attribute from nullable to
// non-nullable when an empty relation child of a Union is removed
UpdateAttributeNullability) :+
// The following batch should be executed after batch "Join Reorder" and "LocalRelation".
其中”Propagate Empty Relations“ 就是上面说到的优化策略,需要看下 AQEPropagateEmptyRelation这个类的源码,做了什么优化
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.optimizer
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.analysis.CastSupport
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions._
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions.Literal.FalseLiteral
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.plans._
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.plans.logical._
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.rules._
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.trees.TreePattern.{LOCAL_RELATION, TRUE_OR_FALSE_LITERAL}
/**
* The base class of two rules in the normal and AQE Optimizer. It simplifies query plans with
* empty or non-empty relations:
* 1. Binary-node Logical Plans
* - Join with one or two empty children (including Intersect/Except).
* - Left semi Join
* Right side is non-empty and condition is empty. Eliminate join to its left side.
* - Left anti join
* Right side is non-empty and condition is empty. Eliminate join to an empty
* [[LocalRelation]].
* 2. Unary-node Logical Plans
* - Limit/Repartition with all empty children.
* - Aggregate with all empty children and at least one grouping expression.
* - Generate(Explode) with all empty children. Others like Hive UDTF may return results.
*/
abstract class PropagateEmptyRelationBase extends Rule[LogicalPlan] with CastSupport {
protected def isEmpty(plan: LogicalPlan): Boolean = plan match {
case p: LocalRelation => p.data.isEmpty
case _ => false
}
protected def nonEmpty(plan: LogicalPlan): Boolean = plan match {
case p: LocalRelation => p.data.nonEmpty
case _ => false
}
protected def empty(plan: LogicalPlan): LocalRelation =
LocalRelation(plan.output, data = Seq.empty, isStreaming = plan.isStreaming)
// Construct a project list from plan's output, while the value is always NULL.
private def nullValueProjectList(plan: LogicalPlan): Seq[NamedExpression] =
plan.output.map{ a => Alias(cast(Literal(null), a.dataType), a.name)(a.exprId) }
protected def commonApplyFunc: PartialFunction[LogicalPlan, LogicalPlan] = {
// Joins on empty LocalRelations generated from streaming sources are not eliminated
// as stateful streaming joins need to perform other state management operations other than
// just processing the input data.
case p @ Join(_, _, joinType, conditionOpt, _)
if !p.children.exists(_.isStreaming) =>
val isLeftEmpty = isEmpty(p.left)
val isRightEmpty = isEmpty(p.right)
val isFalseCondition = conditionOpt match {
case Some(FalseLiteral) => true
case _ => false
}
if (isLeftEmpty || isRightEmpty || isFalseCondition) {
joinType match {
case _: InnerLike => empty(p)
// Intersect is handled as LeftSemi by `ReplaceIntersectWithSemiJoin` rule.
// Except is handled as LeftAnti by `ReplaceExceptWithAntiJoin` rule.
case LeftOuter | LeftSemi | LeftAnti if isLeftEmpty => empty(p)
case LeftSemi if isRightEmpty | isFalseCondition => empty(p)
case LeftAnti if isRightEmpty | isFalseCondition => p.left
case FullOuter if isLeftEmpty && isRightEmpty => empty(p)
case LeftOuter | FullOuter if isRightEmpty =>
Project(p.left.output ++ nullValueProjectList(p.right), p.left)
case RightOuter if isRightEmpty => empty(p)
case RightOuter | FullOuter if isLeftEmpty =>
Project(nullValueProjectList(p.left) ++ p.right.output, p.right)
case LeftOuter if isFalseCondition =>
Project(p.left.output ++ nullValueProjectList(p.right), p.left)
case RightOuter if isFalseCondition =>
Project(nullValueProjectList(p.left) ++ p.right.output, p.right)
case _ => p
}
} else if (joinType == LeftSemi && conditionOpt.isEmpty && nonEmpty(p.right)) {
p.left
} else if (joinType == LeftAnti && conditionOpt.isEmpty && nonEmpty(p.right)) {
empty(p)
} else {
p
}
case p: UnaryNode if p.children.nonEmpty && p.children.forall(isEmpty) => p match {
case _: Sort => empty(p)
case _: GlobalLimit if !p.isStreaming => empty(p)
case _: LocalLimit if !p.isStreaming => empty(p)
case _: Repartition => empty(p)
case _: RepartitionByExpression => empty(p)
// An aggregate with non-empty group expression will return one output row per group when the
// input to the aggregate is not empty. If the input to the aggregate is empty then all groups
// will be empty and thus the output will be empty. If we're working on batch data, we can
// then treat the aggregate as redundant.
//
// If the aggregate is over streaming data, we may need to update the state store even if no
// new rows are processed, so we can't eliminate the node.
//
// If the grouping expressions are empty, however, then the aggregate will always produce a
// single output row and thus we cannot propagate the EmptyRelation.
//
// Aggregation on empty LocalRelation generated from a streaming source is not eliminated
// as stateful streaming aggregation need to perform other state management operations other
// than just processing the input data.
case Aggregate(ge, _, _) if ge.nonEmpty && !p.isStreaming => empty(p)
// Generators like Hive-style UDTF may return their records within `close`.
case Generate(_: Explode, _, _, _, _, _) => empty(p)
case _ => p
}
}
}
/**
* This rule runs in the normal optimizer and optimizes more cases
* compared to [[PropagateEmptyRelationBase]]:
* 1. Higher-node Logical Plans
* - Union with all empty children.
* 2. Unary-node Logical Plans
* - Project/Filter/Sample with all empty children.
*
* The reason why we don't apply this rule at AQE optimizer side is: the benefit is not big enough
* and it may introduce extra exchanges.
*/
object PropagateEmptyRelation extends PropagateEmptyRelationBase {
private def applyFunc: PartialFunction[LogicalPlan, LogicalPlan] = {
case p: Union if p.children.exists(isEmpty) =>
val newChildren = p.children.filterNot(isEmpty)
if (newChildren.isEmpty) {
empty(p)
} else {
val newPlan = if (newChildren.size > 1) Union(newChildren) else newChildren.head
val outputs = newPlan.output.zip(p.output)
// the original Union may produce different output attributes than the new one so we alias
// them if needed
if (outputs.forall { case (newAttr, oldAttr) => newAttr.exprId == oldAttr.exprId }) {
newPlan
} else {
val outputAliases = outputs.map { case (newAttr, oldAttr) =>
val newExplicitMetadata =
if (oldAttr.metadata != newAttr.metadata) Some(oldAttr.metadata) else None
Alias(newAttr, oldAttr.name)(oldAttr.exprId, explicitMetadata = newExplicitMetadata)
}
Project(outputAliases, newPlan)
}
}
case p: UnaryNode if p.children.nonEmpty && p.children.forall(isEmpty) && canPropagate(p) =>
empty(p)
}
// extract the pattern avoid conflict with commonApplyFunc
private def canPropagate(plan: LogicalPlan): Boolean = plan match {
case _: Project => true
case _: Filter => true
case _: Sample => true
case _ => false
}
override def apply(plan: LogicalPlan): LogicalPlan = plan.transformUpWithPruning(
_.containsAnyPattern(LOCAL_RELATION, TRUE_OR_FALSE_LITERAL), ruleId) {
applyFunc.orElse(commonApplyFunc)
}
}
其中关键的注释:
PropagateEmptyRelation can change the nullability of an attribute from nullable to non-nullable when an empty relation child of a Union is removed
Configuration and Enable AQE
1、开启 AQE : spark.databricks.optimizer.adaptive.enabled=true
2、设置Dynamically change sort merge join into broadcast hash join : spark.databricks.adaptive.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold=10M (根据情况设置阈值,我们的kyuubi设置为 10M)
3、开启动态合并:Dynamically coalesce partitions: - spark.sql.adaptive.coalescePartitions.enabled=true - spark.sql.adaptive.advisoryPartitionSizeInBytes=128M - spark.sql.adaptive.coalescePartitions.minPartitionSize=1M - spark.sql.adaptive.coalescePartitions.minPartitionNum=256
4、开启Dynamically handle skew join:(A partition is considered skewed when both (partition size > skewedPartitionFactor * median partition size) and (partition size > skewedPartitionThresholdInBytes) are true) - spark.sql.adaptive.skewJoin.enabled=true - spark.sql.adaptive.skewJoin.skewedPartitionFactor=5 - spark.sql.adaptive.skewJoin.skewedPartitionThresholdInBytes=256M
5、开启Dynamically detect and propagate empty relations:spark.databricks.adaptive.emptyRelationPropagation.enabled=true
在使用 kyuubi 下,有详细的参数配置和说明,参照之前 blog:Kyuubi Overview和部署核心参数调优
补充一下Dynamically Switch Join Strategies中的localShuffleReader
设置 spark.sql.adaptive.localShuffleReader.enabled=true 和将 SortMerge Join 变为 BroadcastHash Join,spark 继续做了优化,通过regular shuffle 变为 localized shuffle,减少网络堵塞的问题。
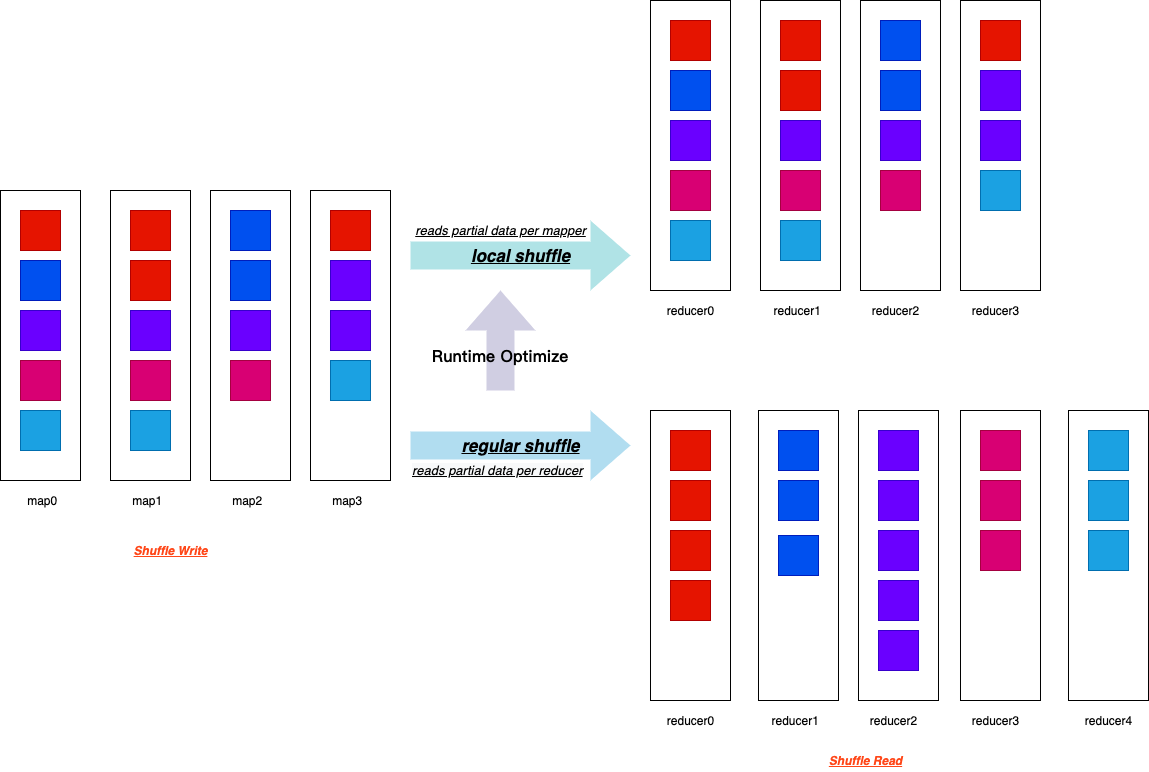
local shuffle 可以从本地存储读取所有重要的数据文件
