Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Kyuubi1.7 Overview和部署核心参数调优
张晓龙 / 2023-04-17
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark3.x 主节点 Master 和 Worker 节点 启动过程分析
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark RPC 架构设计和Akka架构以及基于Spark RPC框架的通信代码演示
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark 2.4 to 3.4 releases notes on spark core and SQL
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark RPC 框架的发展历史和RPC核心类图关系
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark 基础&重要的概念(base and important conception)
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Spark3.x 新特性 AQE的理解和介绍
- 👉 Spark3.x Journey of Discovery | Kyuubi1.7 Overview和部署核心参数调优
The Discovery of Spark 系列文章目前共:7 篇
大数据平台为了”降本增效“,进行 hive to spark 的计算引擎替换。为了更好的使用 spark ,引入 kyuubi 作为中间件,作为提交 spark 任务的入口,管理 spark sesstion 和用户。
下面对 kyuubi 做简单的介绍,以及关键特性解读。 文章内容偏向通识介绍,关于更细节的分析和讨论在其他文章中。
1. kyuubi overview
1.1 是什么
- Kyuubi is a high-performance universal JDBC and SQL execution engine.
- Kyuubi relies on Apache Spark to provide high-performance data query capabilities, Besides, Kyuubi improves ad-hoc responsiveness through the way of engine caching, and enhances concurrency through horizontal scaling and load balancing.
- Kyuubi’s vision is to build on top of Apache Spark and Data Lake technologies to unify the portal and become an ideal data lake management platform.
1.2 架构图 Overview
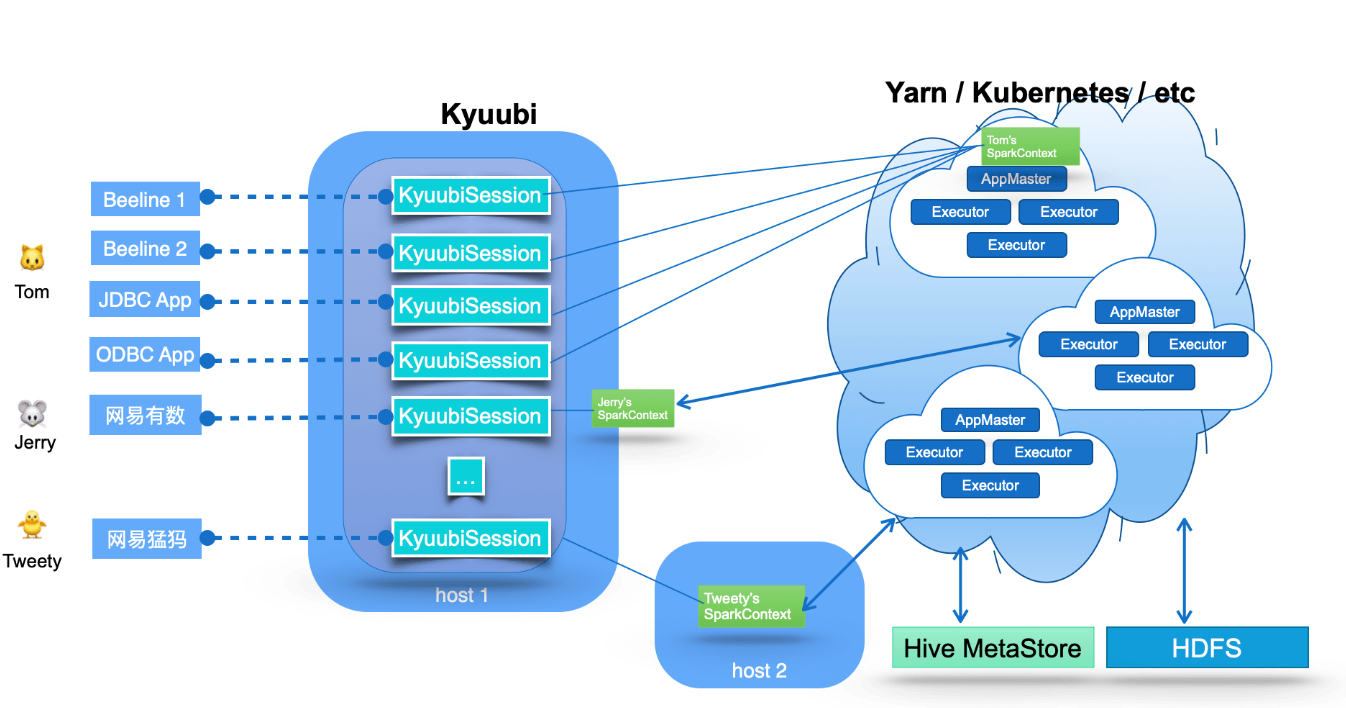
根据架构图,一些核心关键点:
- Within Kyuubi, these connection requests are maintained as the Kyuubi session’s, and execution requests are supported as the Kyuubi Operation’s which are bound to the corresponding sessions.
- These SparkContexts can be Spark programs created locally in client deploy mode by this service instance, or in Yarn or Kubernetes clusters in cluster deploy mode. In highly available mode, these SparkConexts can also be created by other Kyuubi instances on different machines and shared by this instance.
- These programs are implemented on Spark SQL and compile, optimize, and execute SQL statements end-to-end and the necessary interaction with the metadata (e.g. Hive Metastore) and storage (e.g. HDFS) services, maximizing the power of Spark SQL. They can manage their lifecycle, cache and recycle themselves, and are not affected by failover on the Kyuubi server.
- Kyuubi implements the Hive Service RPC module, which provides the same way of accessing data as HiveServer2 and Spark Thrift Server.
- Kyuubi provides a two-level elastic resource management architecture to improve resource utilization effectively
- Kyuubi creates different Spark applications based on the connection requests from the client, and these applications can be placed in different shared domains for other connection requests to share
- Kyuubi does not occupy any resources from the Cluster Manager(e.g. Yarn) during startup and will give all resources back if there is not any active session interacting with a SparkContext.
- Spark also provides Dynamic Resource Allocation to dynamically adjust the resources your application occupies based on the workload.
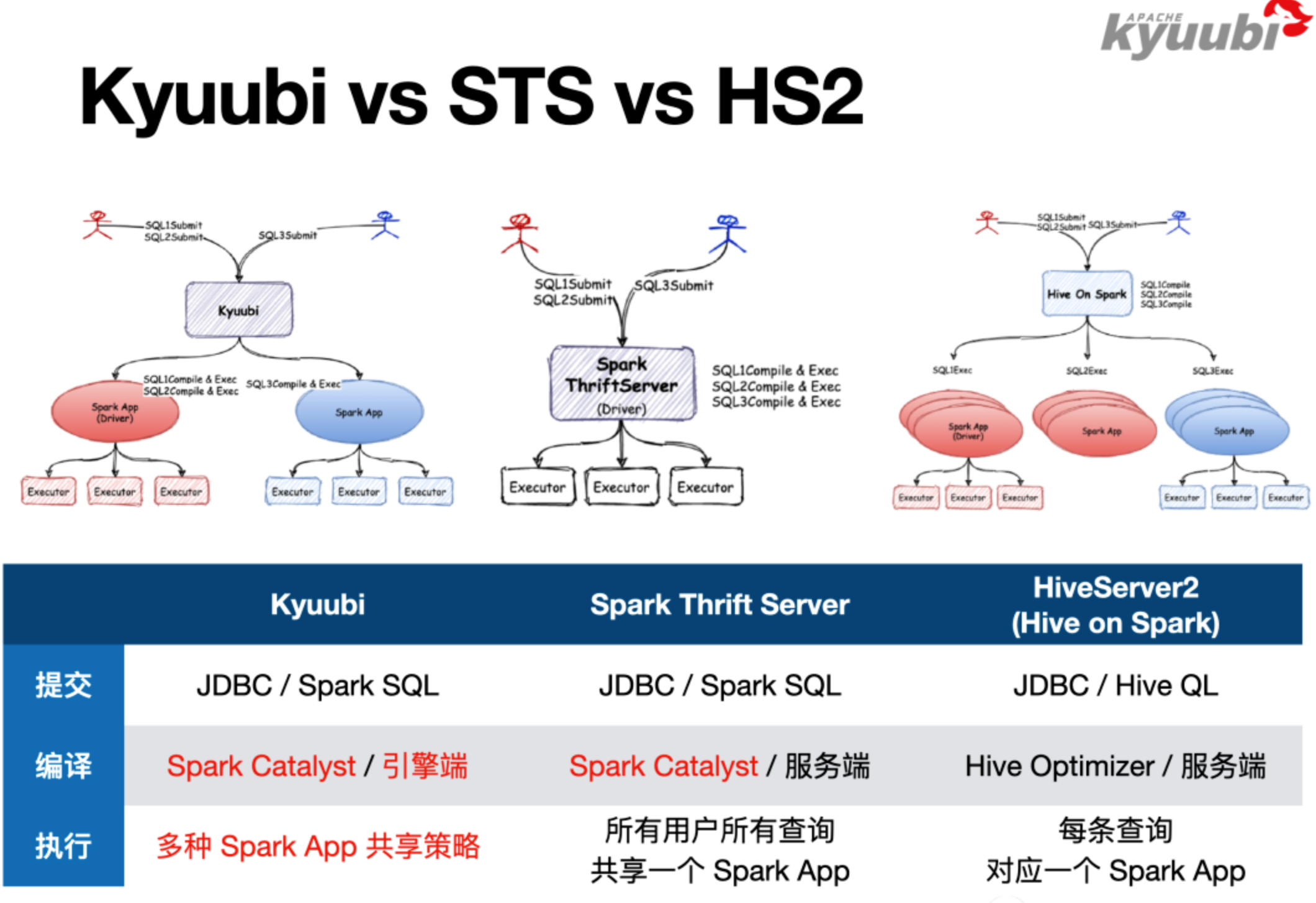
1.3 高可用 & 和其他中间件对比
- Kyuubi provides high availability and load balancing solutions based on Zookeeper, as shown in the following diagram.

- Kyuubi v.s. Spark Thrift JDBC/ODBC Server (STS)
2. Spark 3 特性以及 Kyuubi 带来的增强
2.1 1.7版本技术手册上的基础特性
2.1.1 Deploying Kyuubi
activate config files:
(1)kyuubi-defaults.conf,all Hive primitive configurations,the Spark derivatives。Kyuubi will take these configurations as system wide defaults for all applications it launches.
(2)hive-site.xml,copy from hive-site.xml,single Spark application will automatically load this config file to its classpath,lower priority than kyuubi-default.xml
(3)JDBC Connection URL,pass Hive primitives or Spark derivatives directly in the JDBC connection 。override the defaults for each account user! THIS WORKS ONLY ONCE!!!(when effect in runtime, once!)
2.1.2 share levels
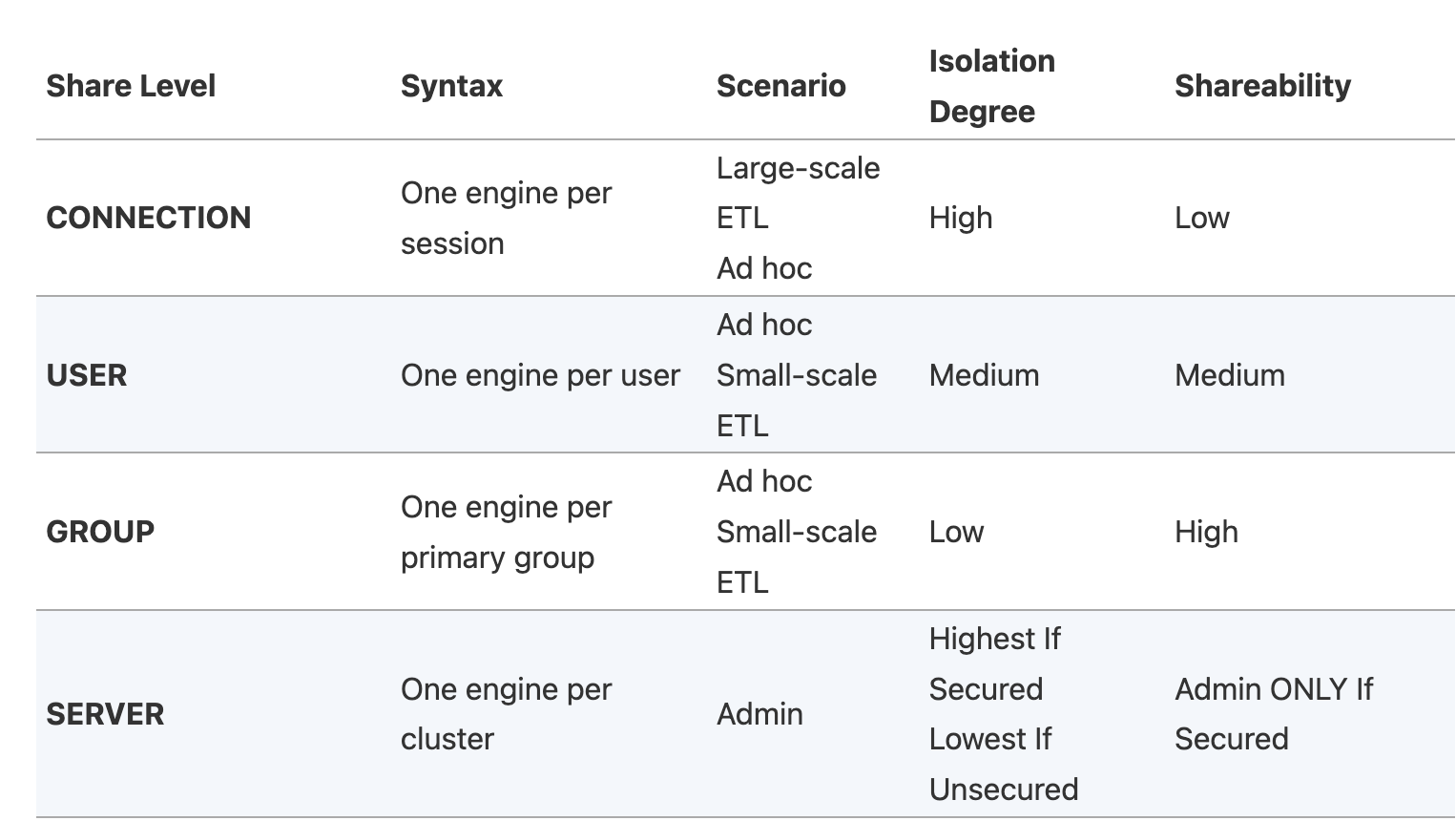
2.1.3 kyuubi engine 的 TTL

2.2 Dynamic Resource Allocation w/ External Shuffle Service)(动态资源分配)
首先是动态资源分配,Spark本身已经提供了Executor的动态伸缩能力。这几个参数配置在语义上是非常明确的,描述了Executor最少能有多少个,最多能有多少个,最大闲置时长,以此控制Executor的动态创建和释放。

引入了Kyuubi后,结合刚才提到的Share Level和Engine的创建机制,我们可以实现Driver的动态创建,还引入了一个参数 engine.idle.timeout,约定Driver闲置了多长时间以后也释放,这样就实现Spark Driver的动态创建与释放。
2.3 Spark Adaptive Query Execution (AQE) & Best Practices for Applying AQE to Kyuubi
例子:
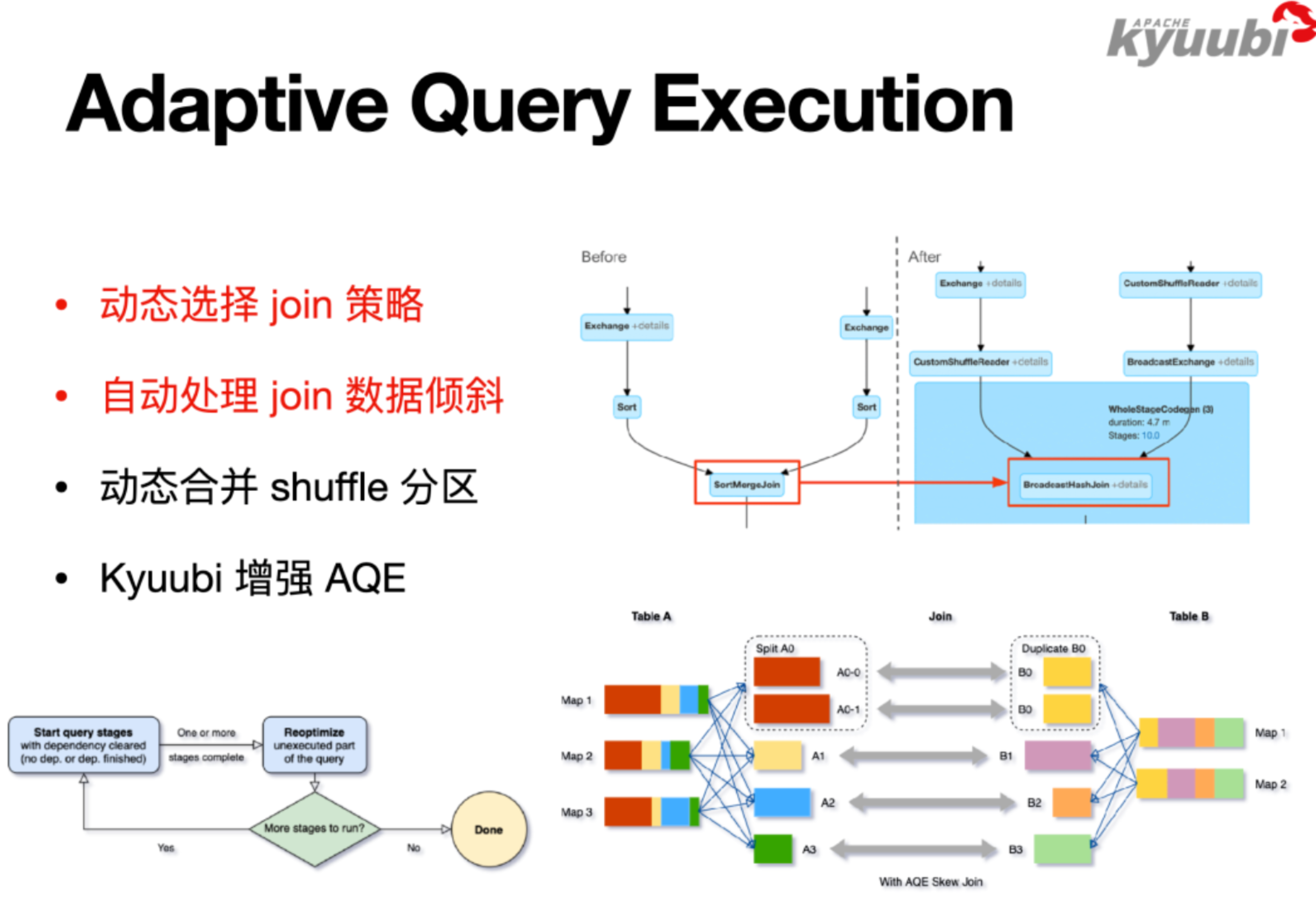
Join作为例子来说,等值的Inner Join,大表对大表做Sort Merge Join,大表对小表做Broadcast Join,但大小表的判断发生在SQL编译优化阶段,也就是在SQL执行之前。
考虑这样场景,
1、两个大表和大表Join,加了一个过滤条件,然后发现跑完过滤条件之后,它就变成了一个大表和一个小表Join了,可以满足Broadcast Join的条件,但因为执行计划是在没跑SQL之前生成的,所以它还是一个Sort Merge Join,这就会引入一个不必要的Shuffle。这就是AQE优化的切入点,可以让SQL先跑一部分,然后回头再跑优化器。
2、另一个典型的场景是数据倾斜。大数据不怕数据量大,但是怕数据倾斜,因为在理想情况下,性能是可以通过硬件的水平扩展来实现线性的提升,但是一旦有了数据倾斜,可能会导致灾难。
是以Join为例,假定是一个等值的Inner Join,有个别的partition特别大,这种场景会有一些需要修改SQL的解决方案,比如把这些大的挑出来做单独处理,最后把结果Union在一起;或者针对特定的Join Key加盐,比如加一个数字后缀,将其打散,但是同时还要保持语义不变,就是说右表对应的数据要做拷贝来实现等价的Join语义,最后再把添加的数字后缀去掉。
可以发现,这样的一个手工处理方案也是有一定规律可循的,在Spark中将该过程自动化了,所以在Spark3里面开启了AQE后,就能自动帮助解决这类Join的数据倾斜问题。如果我们的ETL任务里面有很多大表Join,同时数据质量比较差,有严重的数据倾斜,也没有精力去做逐条SQL的优化,这样情况从HiveQL迁到Spark SQL上面可以带来非常显著的性能提升,10到100倍一点也不夸张!
2.4 Spark通过Extension API提供了扩展能力
Kyuubi提供了KyuubiSparkSQLExtension,利用Extension API在原有的优化器上做了一些增强。
这里列举其中一部分增强规则:
- 其中有Z-order功能,通过自定义优化器规则支持了数据写入时Z-order优化排序的的功能,并且通过扩展SQL语法实现了Z-order语法的支持,也有一些规则丰富了监控统计信息;
- 一些规则限制了查询分区扫描数量,和结果返回数量等。

以RepartitionBeforeWriteHive为例做下简单介绍,这条规则用于解决Hive的小文件写入问题。
对于Hive动态分区写入场景,如果执行计划最后一个stage,在写入Hive表之前,DataFrame的Partition分布与Hive表的Partition分布不一致,在数据写入时,每一个task就会将持有的数据写到很多Hive表分区里面,就会生成大量的小文件。当我们开启RepartitionBeforeWriteHive规则以后,它会在写入Hive表之前依照Hive表的分区插入一个Repartition算子,保证相同Hive表分区的数据被一个task持有,避免写入产生大量的小文件。
Kyuubi为所有规则都提供了开关,如果只希望启用其中部分规则,参考配置文档将其打开即可。
KyuubiSparkSQLExtension提供一个Jar,使用时,可以把Jar拷贝到${SPAKR_HOME}/jars下面,或命令参数–jar添加Jar,然后开启KyuubiSparkSQLExtension,并根据配置项来选择开启特定功能。
2.5 Solution for Big Result Sets(该模式会降低性能)
Kyuubi supports incremental collection mode。This feature is disabled in default, you can turn on it by setting the configuration kyuubi.operation.incremental.collect to true.
该模式会降低性能!
2.6 Z-Ordering Support
To improve query speed, Kyuubi supports Z-Ordering to optimize the layout of data stored in all kind of storage with various data format.

It contains three parties:
Upstream
Due to the extra sort, the upstream job will run a little slower than before
Table
Z-order has the good data clustering, so the compression ratio can be improved
Downstream
Improve the downstream read performance benefit from data skipping. Since the parquet and orc file support collect data statistic automatically when you write data e.g. minimum and maximum values, the good data clustering let the pushed down filter more efficient
This feature is inside Kyuubi extension, so you should apply the extension to Spark by following steps.
add extension jar: copy $KYUUBI_HOME/extension/kyuubi-extension-spark-3-1* $SPARK_HOME/jars/
add config into spark-defaults.conf: spark.sql.extensions=org.apache.kyuubi.sql.KyuubiSparkSQLExtension
Due to the extension, z-order only works with Spark-3.1 and higher version.
2.7 SQL Lineage Support
The current lineage parsing functionality is implemented as a plugin by extending Spark’s QueryExecutionListener.
The SparkListenerSQLExecutionEnd event is triggered after the SQL execution is finished and captured by the QueryExecuctionListener, where the SQL lineage parsing process is performed on the successfully executed SQL.
Will write the parsed lineage information to the log file in JSON format.
3. 参数的配置和调优
基于 kyuubi1.7 版本、结合 spark3.2.1 版本,基于 hadoop2.7 版本,参数调整如下:
yarn 的基本配置(我们 spark 运行在 yarn)
| 配置文件 | 参数 | 值 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| yarn-site.xml | yarn.nodemanager.aux-services | mapreduce_shuffle,spark_shuffle | NodeManager上运行的附属服务。需配置成mapreduce_shuffle、这里添加 spark_shuffle |
| yarn-site.xml | yarn.nodemanager.aux-services.spark_shuffle.class | org.apache.spark.network.yarn.YarnShuffleService | spark shuffle类 |
| yarn-site.xml | spark.shuffle.service.port | 7337 | external 端口 |
| yarn-site.xml | spark.yarn.shuffle.stopOnFailure | false | external shuffle service – external启动 |
| yarn-site.xml | spark.yarn.shuffle.service.metrics.namespace | sparkShuffleService | external shuffle service – 指标监控 |
| yarn-site.xml | spark.yarn.shuffle.service.logs.namespace | external shuffle service – 日志输出 |
spark 基本配置 - shuffle、DRA
| 配置文件 | 参数 | 值 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| spark-default.conf | spark.shuffle.service.enabled | true | 客户端连接external shuffle service |
| spark-default.conf | spark.shuffle.service.port | 7337 | 客户端连接external shuffle service |
| spark-default.conf | spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled | true | 开启动态资源分配 |
| spark-default.conf | spark.dynamicAllocation.executorIdleTimeout | 60s | 回收container的等待时间 |
| spark-default.conf | spark.dynamicAllocation.cachedExecutorIdleTimeout | infinity | 当executor上缓存有数据时,回收等待时间 |
| spark-default.conf | spark.dynamicAllocation.initialExecutors | 2 | 初始executor数量,默认等于minExecutors |
| spark-default.conf | spark.dynamicAllocation.maxExecutors | 60 | 每个Application最⼤并发分配的executor数 |
| spark-default.conf | spark.dynamicAllocation.minExecutors | 1 | 每个Application最⼩分配的executor数 |
| spark-default.conf | spark.dynamicAllocation.executorAllocationRatio | 1 | 最理想的情况下,有多少待执行的任务,那么我们就新增多少个Executor,从而达到最大的任务并发度。但是这也有副作用,如果当前任务都是小任务,那么这一策略就会造成资源浪费。可能最后申请的Executor还没启动,这些小任务已经被执行完了 |
| spark-default.conf | spark.dynamicAllocation.schedulerBacklogTimeout | 1s | 待执行的任务积压超过这个时间,将会请求新的执行者。 |
| spark-default.conf | spark.dynamicAllocation.sustainedSchedulerBacklogTimeout | 1s | 资源不足时,多长时间开始申请executor。 |
| spark-default.conf | spark.dynamicAllocation.shuffleTracking.enabled | true | spark3新增,启用shuffle文件跟踪,此配置不会回收保存了shuffle数据的executor |
| spark-default.conf | spark.dynamicAllocation.shuffleTracking.timeout | infinity | 启用shuffleTracking时控制保存shuffle数据的executor超时时间,默认使用GC垃圾回收控制释放。如果有时候GC不及时,配置此参数后,即使executor上存在shuffle数据,也会被回收。 |
spark 基本配置 - AQE
| 配置文件 | 参数 | 值 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| spark-default.conf | spark.sql.adaptive.enabled | true | 开启 aqe |
| spark-default.conf | spark.sql.adaptive.coalescePartitions.enabled | true | When true and ‘spark.sql.adaptive.enabled’ is true, Spark will coalesce contiguous shuffle partitions according to the target size (specified by ‘spark.sql.adaptive.advisoryPartitionSizeInBytes’), to avoid too many small tasks. |
| spark-default.conf | spark.sql.adaptive.coalescePartitions.initialPartitionNum | 200 | The initial number of shuffle partitions before coalescing. By default it equals to ‘spark.sql.shuffle.partitions’. This configuration only has an effect when ‘spark.sql.adaptive.enabled’ and ‘spark.sql.adaptive.coalescePartitions.enabled’ are both true. |
| spark-default.conf | spark.sql.adaptive.coalescePartitions.minPartitionNum | 200 | |
| spark-default.conf | spark.sql.adaptive.advisoryPartitionSizeInBytes | 64MB | The default value of spark.sql.adaptive.advisoryPartitionSizeInBytes is 64M. Typically, if we are reading and writing data with HDFS, matching it with the block size of HDFS should be the best choice, i.e. 128MB or 256MB. |
| spark-default.conf | spark.sql.adaptive.localShuffleReader.enabled | true | |
| spark-default.conf | spark.sql.adaptive.skewJoin.enabled | true | When true and ‘spark.sql.adaptive.enabled’ is true, Spark dynamically handles skew in sort-merge join by splitting (and replicating if needed) skewed partitions. |
| spark-default.conf | spark.sql.adaptive.skewJoin.skewedPartitionFactor | 10 | |
| spark-default.conf | spark.sql.adaptive.skewJoin.skewedPartitionThresholdInBytes | 256MB |
